 Blend Mode
Blend Mode
The Blend Mode property is available for document content and many of the annotation features in PDF-XChange Editor. It appears in the Properties Toolbar when objects that feature it are selected, and can also be viewed/edited in the Properties pane. Blend Mode determines how content blends with overlapping content. The Fill Color property is referenced when Blend Modes are used, and this can be edited in the Properties Toolbar or the Properties pane:
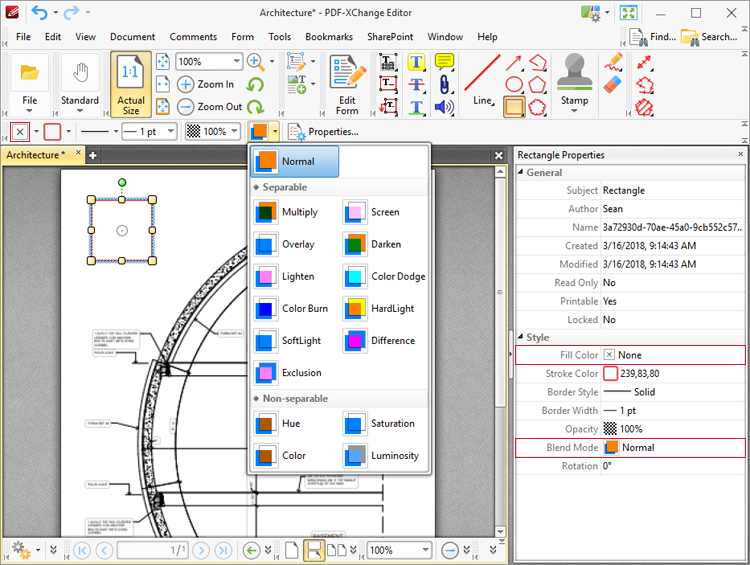
Figure 1. Blend Mode Options
•Normal maintains the selected Fill Color.
•Multiply multiples the Fill Color value with the color value of the underlying content. Resultant colors are at least as dark as one of the source colors.
•Screen multiplies the complements of the Fill Color value with the color value of underlying content and then complements the result. The resulting color will be at least as light as one of the source colors.
•Overlay either multiplies or screens the Fill Color value with the color value of underlying content, depending on the color value of the latter. The Fill Color will overlay the underlying content while preserving its highlights and shadows. The color of underlying content will be blended with the Fill Color to reflect its shade.
•Darken selects the darker of the Fill Color value and the color value of underlying content.
•Lighten selects the lighter of the Fill Color value and the color value of underlying content.
•Color Dodge brightens the color of the underlying content to reflect the Fill Color. Note that if black is used as the Fill Color then there will be no effect.
•Color Burn darkens the color of the underlying content to reflect the Fill Color. Note that if white is used as the Fill Color then there will be no effect.
•Hardlight either multiples or screens the Fill Color value with the color value of underlying content, depending on the Fill Color value. This creates the effect of shining a strong spotlight on the underlying color.
•Softlight either darkens or lightens colors, depending on the Fill Color value. This creates the effect of shining a diffused spotlight on the underlying color.
•Difference subtracts the darker of the constituent colors from the lighter color.
•Exclusion performs a less contrasted version of the Difference option.
•Hue combines the Fill Color value with the saturation and luminosity of the color value of the underlying content.
•Saturation combines the saturation of the Fill Color with the hue and luminosity color value of the underlying content.
•Color combines the the hue and saturation of the Fill Color with the luminosity color value of the underlying content.
•Luminosity combines the luminosity of the Fill Color with the hue and saturation of the color value of the underlying content.
Note that the Arrange feature can be used to change the layer order of overlapping content, which has a direct effect on the Blend Mode. Right-click content and click Arrange to view options:
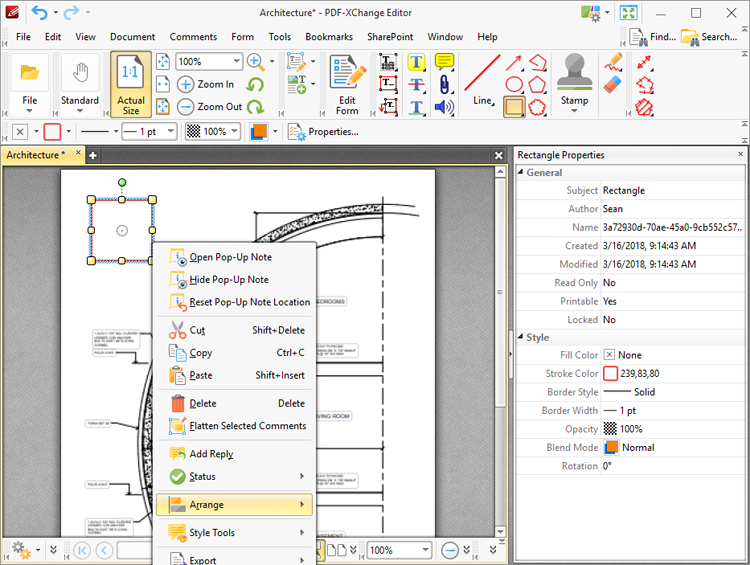
Figure 2. Content Items Shortcut Menu, Arrange
The following options are available:
•Bring Forward, which brings the selected content up a step in cases where multiple items overlap.
•Send Backward, which sends the selected content back a step in cases where multiple items overlap.
•Bring to Front, which brings the selected content to the top in cases where multiple items overlap.
•Send to Back, which sends the selected content to the back in cases where multiple items overlap.
Examples
The image below details sixteen copies of the same group of comments - a blue circle annotation placed over a yellow circle annotation placed over a red circle annotation. The Blend Mode is set to normal:
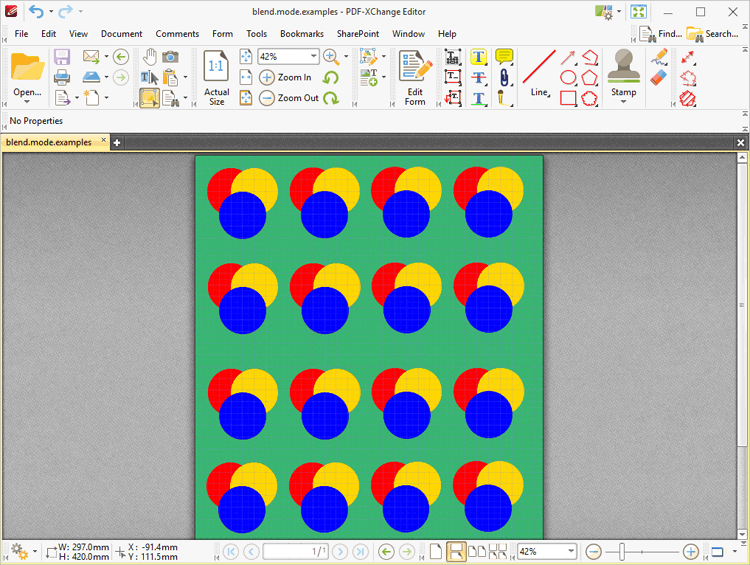
Figure 3. Blend Mode Examples
The effect of selecting each group of comments and applying one of the blend modes is detailed in the image below:
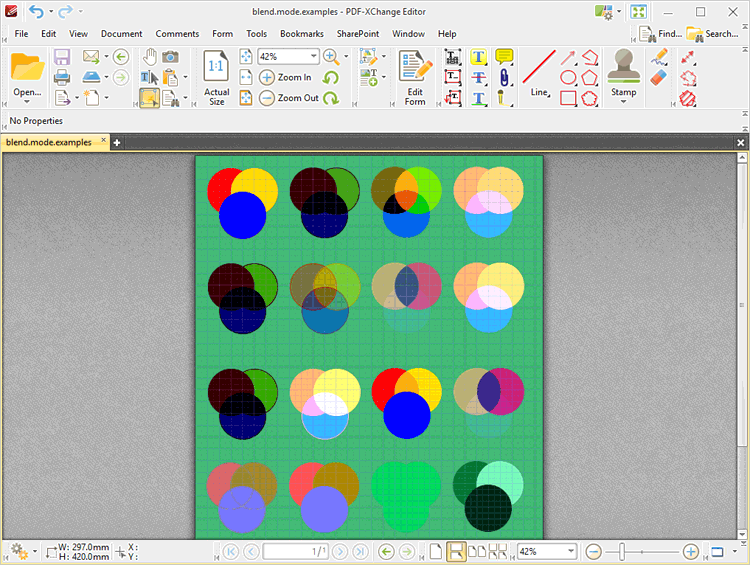
Figure 3. Blend Mode Examples
The Blend Modes applied, from left to right and top to bottom, are: Normal, Multiply, Overlay, Lighten, Color Burn, SoftLight, Exclusion, Screen, Darken, Color Dodge, Hardlight, Difference, Hue, Color, Saturation and Luminosity. Note that the green background has a direct effect on the blend mode output. If the background color is changed then the blend mode output updates accordingly:
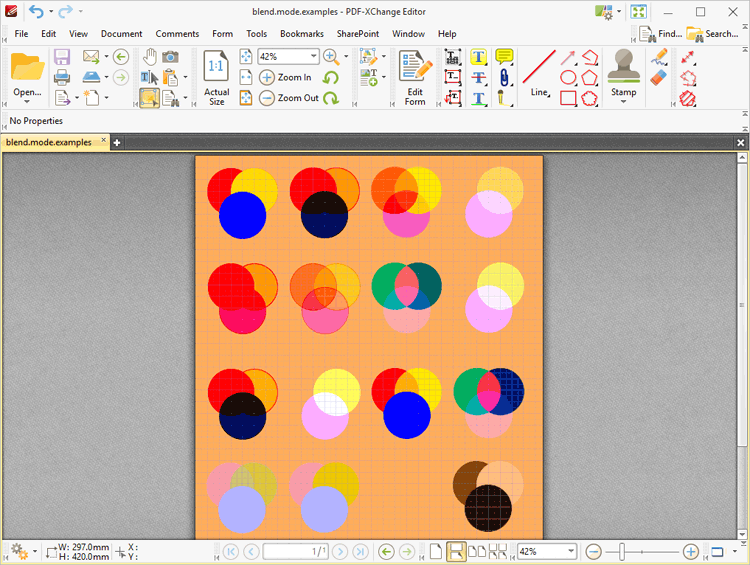
Figure 4. Blend Mode Examples, Updated Background